Given the rather high energy prices, heating a house during the cold season is quite expensive, so many are looking for an alternative to gas and electricity. Fuel pellets are a modern, environmentally friendly and economical type of fuel. Using them for heating reduces heating costs by 3-4 times.

What are pellets?
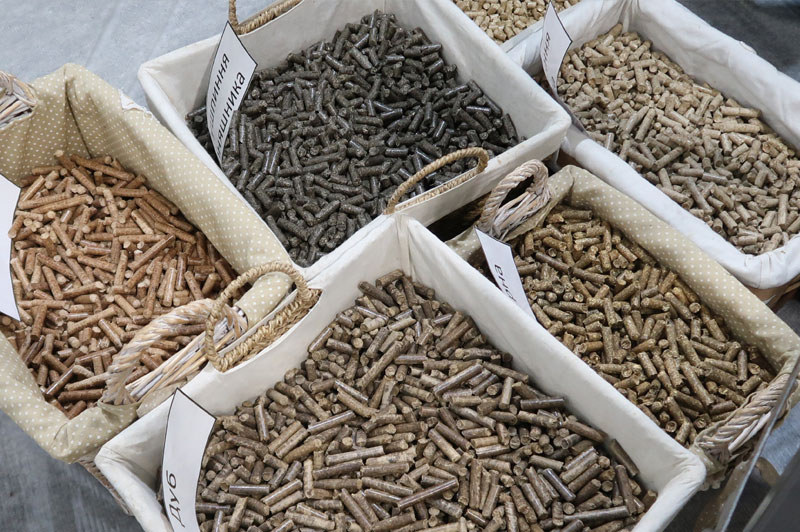
Pellets are called granulated fuel. They are produced from waste products from the woodworking and agricultural industries. Outwardly, pellets look like cylinder-shaped pellets, up to 8 mm in diameter and up to 7 cm long. The size of the pellets depends on what material the pellet is made of and what boiler it is intended for.
The cost-effectiveness of use is explained by the high efficiency of fuel pellets, they emit 1.5-2 times more thermal energy in comparison with firewood and other energy carriers and can be used in pyrolysis boilers. Such fuel has been actively used for a long time in automated household and industrial boiler houses abroad, and recently it has become more and more popular in Ukraine.
The use and production of pellets allows you to maintain the stability of the environment. Since this type of fuel is produced from waste, it absolutely does not harm humans and the environment and emits a minimum amount of CO2 equal to the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by wood. Moreover, the transition to pellet fuel allows you to save forests and not pollute nature with waste from the woodworking industry, and its atmospheric emissions are many times safer than burning coal and fuel oil.
Depending on the raw materials used, the following types of pellets are distinguished:
- White (premium) – made from wood waste (without bark) and have the highest calorific value, practically do not leave ash, are suitable for boilers of all types.
- Industrial – made from low quality wood, containing, in addition to waste, bark and a certain amount of non-combustible particles, due to the presence of which more frequent cleaning of boilers is required.
- Agropellets are made from agricultural waste and have a lower calorific value compared to wood pellets, as well as a high ash content (from 4% and above), which is why they are used mainly at large thermal power plants or in boilers with automatic cleaning. Such pellets are the most affordable.